SUMMARY:
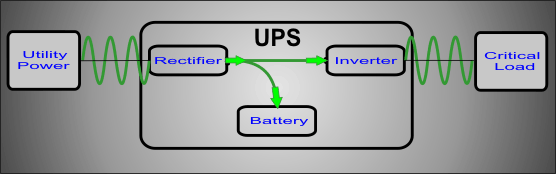
In Normal Operation all equipment is operating with no disturbances, faults or problems. AC (alternating current) from utility, often called commercial power, is fed to the UPS’s Rectifier section. The Rectifier takes the AC and converts it to DC (direct current) for 2 purposes.The first purpose is to feed the Inverter section with DC. Here it is converted back to AC to supply the critical load, sensitive equipment, with a constant regulated AC output that is provided to keep sensitive electronic equipment functioning. Depending on size and type of the UPS in mention, the output of the UPS can be 120 VAC(1Φ), 208 VAC or 480 VAC(3Φ) in the US. The second purpose of the DC is to feed the Battery section where it takes the DC from the Rectifier and usees it to charge the batteries in this mode of operation.
As depicted above the Inverter and Battery sections share the same common DC output source from the Rectifier. The importance of supplying DC to the Inverter and Battery sections is significant in the proper operation of a double conversion UPS. The battery section takes the DC from the DC Bus and uses it to charge its batteries during a steady state of operation. Click on the other modes of operation buttons above to see how a UPS behaves in other scenarios.
Protect Your Investment with InLine Power

